As the prospect of living and working in space becomes more of a reality, the private sector has started investing in emerging technologies in manufacturing that will aid this transition.
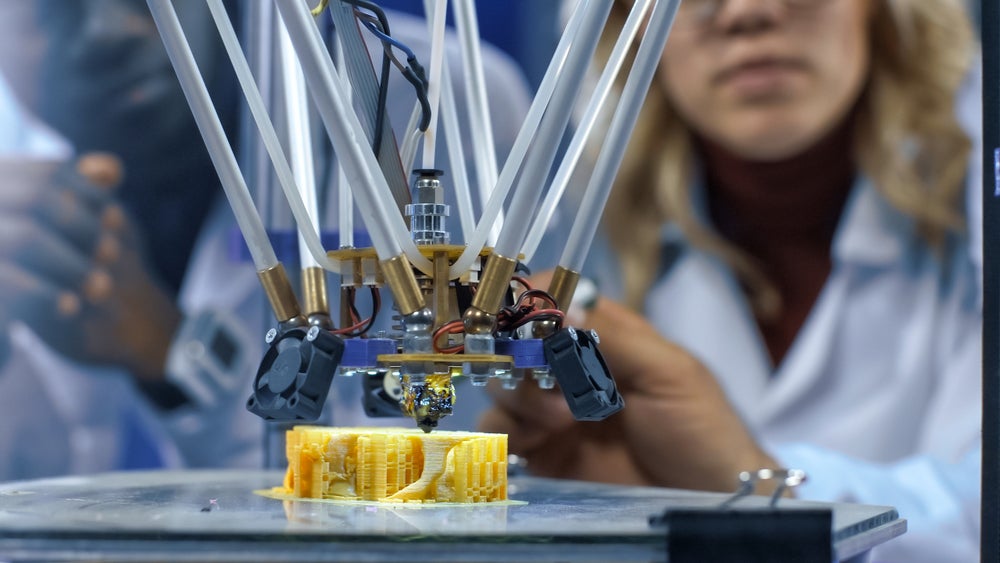
3D printing is at the centre of these advancements, with ICON Technologies developing 3D-printed houses on the Moon and Photocentric developing a 3D printer for in-space manufacturing.
In-space manufacturing
One of the big hurdles facing companies is the cost of reaching space. SpaceX is currently charging an estimated $67 million per launch of the Falcon 9, while Arianespace charges between $165 million and $220 million per launch of the Ariane 5. While launching costs are likely to decrease in the coming years, transporting anything into space will remain astronomically expensive.
The ability to colonize space will depend on the development of on-demand manufacturing capabilities for long-term presence in space. And while this seems like a distant dream, it is closer than we think. Many start-ups are already working on technologies that will help us address issues of resource limitation and the operational efficiency of in-orbit operations.
In September 2023, the European Space Agency (ESA)’s in-orbit manufacturing accelerator program invested in two 3D printing companies, Photocentric and DCUBED, who are both working to improve space manufacturing capabilities. Photocentric is developing a resin-based 3D printer for in-space manufacturing, while DCUBED is focused on producing 3D-printed solar arrays for in-orbit power generation. Another 3D printing company, ICON Technologies, is also developing technologies to build 3D-printed houses on the Moon.
The theory among experts is that 3D printing will be a cheaper alternative to transporting cargo to space, and will provide on-demand manufacturing, thus easing astronauts’ dependency on deliveries from Earth.
How well do you really know your competitors?
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Thank you!
Your download email will arrive shortly
Not ready to buy yet? Download a free sample
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
By GlobalDataThe benefits of microgravity
There is already some manufacturing happening in space, albeit on a very small scale.
Space offers a unique research and manufacturing environment with zero gravity, a near vacuum, and high radiation levels, providing better control of liquid and gas materials and improved sediment separation.
In theory, the absence of sedimentation in microgravity enables researchers to combine any number of substances that would normally be extremely challenging or impossible to mix evenly on Earth.
Most current microgravity manufacturing providers are small-scale manufacturers for the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. The practice is relatively costly, however; advances in microgravity manufacturing will be essential in understanding how, in the future, 3D printers will operate in space environments.