Summary Bullets:
- Past attempts to build private networks were fragmented, made up of disparate proprietary networks, and were often lacking in performance, reliability and security – 5G changes all that.
- Private Networks account for most current enterprise 5G adoption, with verticals such as manufacturing, transportation, logistics, healthcare, and utilities leading the way forward.
5G is the highly anticipated next generation of mobile communications technology, but is still at the early stage of network deployment and market development. This blog looks at the adoption of 5G Private Networks for and business/enterprise markets.
Market Landscape:
The initial use cases for private networks have been focused on campus and site connectivity, and are for the most part separate from the public network – for reasons such as security and the desire for greater control over data integrity and transmission. Past attempts at implementing private networks were fragmented, made up of disparate proprietary networks, and were deficient in performance, reliability and security; but 5G changes the playing field significantly by bringing increased throughput, support for low (10ms or less) millisecond-range latencies. The potential for massive device connectivity, enhanced security and deterministic performance that rivals the capabilities and reliability of wired networks have all been aided by rigorous industry standards and a vibrant ecosystem.
Market Forecasts:
Market forecasts paint a rosy future for private networks, prompting vendors to step up with tailored solutions, in most cases different than those deployed by large telcos. Network operators view the private networks opportunity as a way to increase their market appeal by offering flexible and high value services to enterprises that will greatly increase their revenues and profitability. Private Networks represents one of the highest networking growth sectors with multiple forecasts pointing to be an aggregate $60 billion industry over the next five years. (e.g., GSMA, 5G Americas, others). The market is being driven by demands from the Utilities, Oil and Gas, and Manufacturing sectors. Few operators have launched standardized commercial B2B services, but instead are leveraging their networking and managed services capabilities to deliver customized opportunities for private 5G.

Private Network Use Cases and Characteristics
Capturing the private network market represents a big win-win for enterprises and telcos; but doing so requires new capabilities from the network – this is where 5G really comes into focus. There are new application requirements and a host of ecosystem and application enablers needed to satisfy private network demands.
Application Requirements:
- High level of security and privacy – data integrity and control are paramount
- Mobility and flexibility – needed to support an increasingly mobile workforce
- Guaranteed coverage and selectable bandwidth – delivering when and where it’s needed
- Granular control – user portals and the ability to control and monitor all aspects of the network
- Ease of deployment – automated and near real-time network turn-up and out-of-the-box solutions
Application Enablers:
- Adequate spectrum – dedicated, unlicensed, enterprise owned
- Dedicated LTE/5G infrastructure – leverage LTE where >10 ms latency is adequate
- URLLC components – edge, AI, smart industrial machines/tools
- Public 4G/5G for hybrid cloud solutions – cloud is an integral requirement and requires seamless integration
- Professional & managed services – enterprises need to reduce barriers to design, develop and deploy
- Addressing the Skills Gap – “ready to go” pre-packaged and pre-tested solutions
Use Case Examples:
- Campus/site network for constrained locations – the classical use case
- Hybrid private/public cloud – guaranteeing coverage and service assurance
- Mission-critical – control for real-time applications and high availability
Private Network Deployment Models:
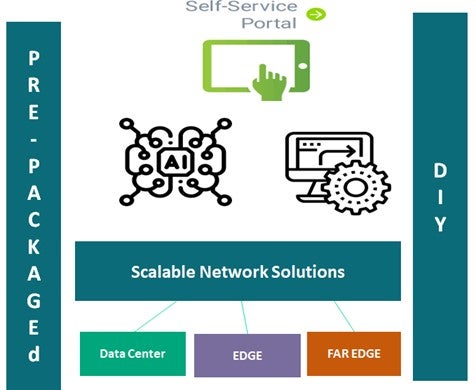
There are multiple deployment models developing for the private network market. One leverages components selected by the operator or enterprise and integrated into an end-to-end solution – the DIY model; the other leverages a pre-integrated and pre-tested solution provided as a turn-key or near turn-key package by a vendor or system integrator. Both models have merit given the capabilities of the operator/enterprise, and the time frame to deploy. Pre-packaged solutions are gaining in popularity, especially if they can be customized to meet exacting use case standards. Vendors are providing a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) model that can be extended by ecosystem partners to deal with unique requirements of the various vertical market use cases.
Operators/Enterprises want tools to ease the complexity – either pre-integrated or components (DIY) – depending on Skill Sets.
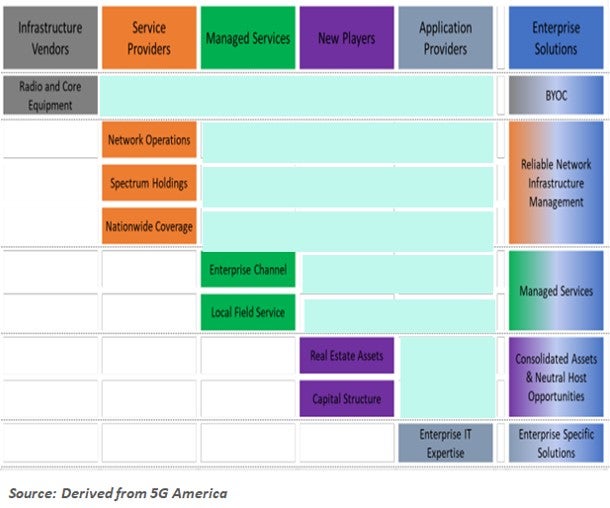
5G Ecosystem Key Contributors
The 5G Private Network market offers opportunities for all sectors of the ecosystem:
- Infrastructure vendors, for example can provide the programmable infrastructure to support DIY and/or pre-integrated platforms.
- Service providers hold the keys to management operations, spectrum and footprint – and can build on vendor solutions.
- Managed service providers tie the network resources together with custom and standard services.
- New players bring unique assets and capabilities to the table, for example unique vertical market knowledge, outside funding, physical assets, such as spectrum or right of ways.
- Applications and OTT suppliers bring unique enterprise and vertical market expertise to the table based on deep understanding of market.
The following graphic demonstrates the full private network deployment landscape and related contributing entities.
Recommendations and Observations:
- Vendors should provide pre-packaged/configured and self-installable solutions to drive 5G Private Network adoption, especially as carriers bring offerings into markets where there are competitive alternatives. Vendors such as ZTE have stepped up to offer an “All-in-One Private 5G Solution” that, includes 5G RAN, PON access, optical & IP, core network and edge cloud, to empower 5G capabilities and on-demand cloud services.
- Operators need to be consistently developing eMBB 5G use cases, both for early applications and for ultra-low latency and gigabit data speeds. These use cases need to be ready as their networks evolve – starting in earnest in 2021.
- Operators should work to fill in the gap when it comes to sporting and entertainment events to bring users close to the action – such as 4K video, and flexible on-site solutions.
- Network slicing and the advent of private networks are closely allied with telco edge strategies because they add commercial flexibility, as well as the ability to keep data local and empower customers with dedicated bandwidth for high availability, reliability, security, and low latency.
- Vendors and Operators need to build an ecosystem and partner roster to drive integrated experiences and provide incubators for innovative on-the-go experiences that take advantage of 5G.
- For gaming applications, operators should be open to forming partnerships with OTT providers that have gaming expertise – include white label agreements, simple connectivity arrangements, and deals that involve more network elements, such as MEC.
- Multiple 5G private network trials are underway, and the pace of adoption has accelerated in 2021, with the second half of the year expected to deliver many more examples and success stories related to 5G private network adoption.
- Private wireless networks have become a hotly contested space because businesses that are often in location-constrained verticals such as manufacturing plants, campuses, transportation hubs, or field sites for mining or utilities are increasingly looking to cellular connections for flexibility, mobility, relief from heavy cables and spaghetti-like wiring arrangements, and eventually support for the kinds of low latency businesses will need for technologies and use cases such as AR/VR, robotics, real-time data and video collection and analytics, and autonomous vehicles.


