Leading AI companies such as OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft have a distinct advantage when accessing the high-quality training data needed to develop more sophisticated and capable AI models.
This advantage stems from their existing data-rich platforms, and access to the necessary funding to license high-quality data for AI model training. However, this creates a competitive landscape that poses significant challenges for smaller AI companies and has various implications for consumers.
Access to data, and its advantages
Meta (formerly Facebook) has access to an immense amount of data through its platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp. This allows Meta to train models on real-world human behavior and language.
Similarly, Microsoft accumulates a wealth of data through its services such as LinkedIn, Office 365, and Azure. OpenAI has partnerships and collaborations (such as with Microsoft for Azure) that provide it with substantial computing power and datasets necessary for training state-of-the-art models like GPT-4. OpenAI has spent hundreds of millions on licensing content, a budget smaller companies and nonprofits simply cannot match.
The power of high-quality training data is a crucial factor in the performance of AI models. Rich, diverse datasets allow for more comprehensive training, reduce biases, and improve generalisation across different tasks. The sheer quantity and quality of data that leading AI companies possess allow for the creation of models that can perform a wide array of tasks, from conversational agents to complex predictive analytics. Research, including an article published on data.europa.eu, is increasingly demonstrating that the availability of high-quality training data is important in making sophisticated AI models.
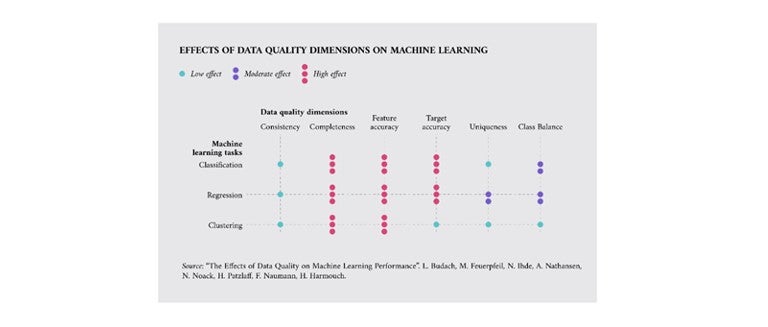
Figure 1: The effect of data quality on the performance of AI algorithms. (GitHub)
How well do you really know your competitors?
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Thank you!
Your download email will arrive shortly
Not ready to buy yet? Download a free sample
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
By GlobalDataFor example, OpenAI’s models benefit from a combination of public and proprietary datasets, enabling their leading AI models, such as GPT-4o, to understand and generate human-like text with remarkable proficiency. Companies including Meta, Google, Amazon, and Apple have made lucrative deals with companies including Reddit and Shutterstock to access hundreds of millions of images and videos for training. However, there are concerns about whether data for AI model training is always accessed ethically or legally. In 2023, the New York Times sued OpenAI and its partner, Microsoft, for copyright infringement.
Impact on smaller AI companies
Smaller AI companies face significant hurdles due to the disparity in access to high-quality training data. Without the extensive resources of tech giants, smaller firms often struggle to obtain and process large datasets. This creates a barrier to entry, limiting innovation and competition in the AI field. These companies might rely on publicly available datasets or third-party data providers, which may not match the scale and quality of data accessible to larger players. Publicly available datasets are often limited in scope and diversity compared to datasets used by leading AI companies.
This leads to a competitive imbalance where only well-funded companies can afford to keep developing AI technologies, which could potentially stifle diversity in AI development. This concentration of power also raises concerns about data privacy, ethical use of AI, and market monopolisation. Consumers may face reduced choices, which can lead to a less competitive market, and potentially higher prices.
Additionally, the extensive data collection practices of these large companies often provoke privacy concerns, as users’ data is continually harvested to train and refine AI models. For example, Meta controversially changed its privacy policy, allowing it to use years of users’ personal posts for AI training—including private images—all without asking for user consent. To further complicate matters, Meta may still process information about people who do not use its products and services nor have an account if they appear in an image or are mentioned in posts or captions shared by a user.
To date, Meta has received 11 EU complaints from the European Center for Digital Rights—also known as NOYB (“None of Your Business”). A spokesperson for Meta commented: “We are confident that our approach complies with privacy laws, and our approach is consistent with how other tech companies are developing and improving their AI experiences in Europe (including Google and Open AI).”
Increased access to high-quality training data enables leading AI companies such as OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft to develop better AI models. While this drives innovation and improves consumer experiences, it also creates significant challenges for smaller companies that cannot afford data licenses and raises important ethical and privacy issues. As the AI landscape evolves, balancing innovation with fair competition and consumer rights remains a critical challenge for the future of ethical AI development.








Related Company Profiles
Meta Platforms Inc
Microsoft Corp
LinkedIn Corp
Azure Power Global Ltd
Google LLC